Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Li, L.*; Miyamoto, Goro*; Zhang, Y.*; Li, M.*; Morooka, Satoshi; Oikawa, Katsunari*; Tomota, Yo*; Furuhara, Tadashi*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 184, p.221 - 234, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Sr in highly radioactive aqueous samples via conversion to a kinetically stable 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid complex followed by concentration-separation-fractionation based on capillary electrophoresis-liquid scintillation
Sr in highly radioactive aqueous samples via conversion to a kinetically stable 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid complex followed by concentration-separation-fractionation based on capillary electrophoresis-liquid scintillationOuchi, Kazuki; Haraga, Tomoko; Hirose, Kazuki*; Kurosawa, Yuika*; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Shibukawa, Masami*; Saito, Shingo*
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1298, p.342399_1 - 342399_7, 2024/04
Given that conventional methods of high-dose sample analysis pose substantial exposure risks and generate large amounts of secondary radioactive waste, faster procedures allowing for decreased radiation emission are highly desirable. To address this need, we developed a  Sr
Sr quantitation technique that is based on liquid scintillation counting-coupled capillary transient isotachophoresis (ctITP) with two-point detection and relies on the rapid concentration, separation, and fractionation of 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-complexed
quantitation technique that is based on liquid scintillation counting-coupled capillary transient isotachophoresis (ctITP) with two-point detection and relies on the rapid concentration, separation, and fractionation of 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-complexed  Sr
Sr in a single run. This method, which allows for the handling of high-dose radioactive specimens at the microliter level and is substantially faster than conventional ion-exchange protocols, was used to selectively quantify
in a single run. This method, which allows for the handling of high-dose radioactive specimens at the microliter level and is substantially faster than conventional ion-exchange protocols, was used to selectively quantify  Sr
Sr in real high-dose waste. The successful concentration-separation in ctITP was ascribed to the inertness of the Sr-DOTA complex to dissociation.
in real high-dose waste. The successful concentration-separation in ctITP was ascribed to the inertness of the Sr-DOTA complex to dissociation.
Ito, Takashi; Kadono, Ryosuke*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044602_1 - 044602_7, 2024/04
Murakami, Kenta*; Onizawa, Kunio; Yamamoto, Akio*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 66(4), p.199 - 202, 2024/04
, 66(4), p.199 - 202, 2024/04
The Standards Committee of Atomic Energy Society of Japan has been leading activities related to long-term operation through the revision of the Code of Practice for Aging Management, and we believe that we must continue to make important contributions in light of recent changes in laws and regulations. This paper recapitulates the discussions in the special session conducted at the 2023 fall meeting, and describes the efforts toward safe long-term operation and the points to keep in mind in the standardization of such activities. The important points are (1) to make effective use of knowledge found over time, (2) not to overlook new knowledge that has a significant impact on safety, including obsolescence, (3) to assign a level of importance to the response based on the impact on safety and the likelihood of its occurrence, and (4) to contribute to the establishment of an international knowledge base.
Kamikawa, Yutaka; Suzuki, Makoto; Agake, Toshiki; Murakami, Takahiko; Morita, Yusuke; Shiina, Hidenori; Fukushima, Manabu; Hirane, Nobuhiko; Ouchi, Yasuhiro
JAEA-Technology 2023-030, 57 Pages, 2024/03
Owing to the publication of the latest data about aircraft crashes by Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA), it was necessary to re-evaluate the probabilities of aircraft crashes for Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI). By using of the assessment method provided in "Regulatory Guide of the Assessment Standard for Probability of Airplane Crash on a Nuclear Power Reactor Facility", we re-evaluated the probabilities of aircraft crashes against the nuclear facilities in NSRI. As a result of the evaluations, the sum of the probabilities of aircraft crashes against Waste Treatment Facilities (maximum probability among all nuclear facilities in NSRI) is 5.68 10
10 (times/(reactor
(times/(reactor  year)) which is lower than 10
year)) which is lower than 10 (times/(reactor
(times/(reactor  year)) that is the assessment criterion whether aircraft crashes is considered to be "anticipated external human induced events" in design basis or not.
year)) that is the assessment criterion whether aircraft crashes is considered to be "anticipated external human induced events" in design basis or not.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Sasaki, Miyuki; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Akutsu, Yuichiro*; Arai, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-026, 161 Pages, 2024/03
By the accident at Tokyo Electric Power Company's (TEPCO's) Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), caused by tsunami triggered by the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake, a large amount of radioactive material was released into the surrounding environment. After the accident, Airborne Radiation Monitoring (ARM) via manned helicopter has been utilized as a method to quickly and extensively measure radiation distribution surrounding FDNPS. In order to utilize ARM and to promptly provide the results during a nuclear emergency, information on background radiation levels, topographical features, and controlled airspace surrounding nationwide nuclear facilities have been prepared in advance. In the fiscal year 2022, we conducted ARM around the Mihama Nuclear Power Station of Kansai Electric Power Company (KEPCO), the Tsuruga Power Station of Japan Atomic Power Company (JAPC), and the Ikata Power Station of Shikoku Electric Power Company (YONDEN), and prepared information on background radiation doses and controlled airspace. In addition, we have developed an aerial radiation detection system via unmanned airplane, which is expected to be an alternative to ARM, during a nuclear emergency. This report summarizes the results and technical issues identified.
Group for Fukushima Mapping Project
JAEA-Technology 2023-024, 176 Pages, 2024/03
This report presents results of the investigations on the distribution-mapping project of radioactive substances owing to TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) conducted in FY2022. Car-borne surveys, a measurement using survey meters, a walk survey and an unmanned helicopter survey were carried out to obtain air dose rate data to create their distribution maps, and temporal changes of the air dose rates were analyzed. Surveys on depth profile of radiocesium and in-situ measurements as for radiocesium deposition were performed. Based on these measurement results, effective half-lives of the temporal changes in the air dose rates and the deposition were evaluated. Score maps to classify the importance of the measurement points were created, and the factors causing changes in the score when monitoring data from multiple years were used were discussed. The range of fluctuation of past tritium concentration data in seawater was determined, and the causes of the fluctuation were discussed. Monitoring data in coastal area performed in 2022 owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan was summarized, and temporal changes in cesium-137 were analyzed. Using the Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach, we obtained maps that integrated air dose rate distribution data acquired through surveys such as car-borne and walk surveys with respect to the region within 80 km from the FDNPS and Fukushima Prefecture. The measurement results for FY2022 were published on the "Database for Radioactive Substance Monitoring Data", and measurement data were stored as CSV format. Radiation monitoring and analysis of environmental samples owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan were carried out.
Togawa, Orihiko; Okuno, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2023-043, 94 Pages, 2024/03
In order to translate nuclear disaster prevention documents written in Japanese into English, the Basic Act on Disaster Management, the Act on Special Measures Concerning Nuclear Emergency Preparedness, and the Convention on Nuclear Safety were surveyed for corresponding terms in Japanese and English. The survey results were integrated and unified English translations were selected. As a result, a Japanese-English correspondence table of technical terms in the field of nuclear disaster prevention was prepared and proposed.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2023-030, 80 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of a cooperative operation robot system for radiation source exploration" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to develop a Cooperative Operation Robot system for RAdiation Source Exploration (CORRASE). The multiple robot system provides radiation source exploration with wide field of view, rapidity, and low cost. The radiation source exploration is realized with multiple robots carrying directional gamma-ray detectors determining the incident direction of the incoming gamma-rays. We will develop the system by the final year of this proposal aiming for application in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Hokkaido University*
JAEA-Review 2023-027, 126 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Study on rational treatment/disposal of contaminated concrete waste considering leaching alteration" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to understand migration behaviors of radionuclides in relation to the properties of concrete altered by leaching, to develop migration model of radionuclides, and to evaluate waste management scenarios, focusing on underground concrete structures in contact with contaminated water.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2023-025, 117 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of extremely small amount analysis technology for fuel debris analysis" conducted in FY2022. Understanding the properties of fuel debris is necessary for handling, criticality control, storage control, etc. A key technique is the chemical analysis of actinide nuclides. We develop sample pretreatment technology and separation / analysis process required for chemical analysis. The purpose of this study is to streamline future planned fuel debris analysis. To promote 1F decommissioning, we will train human resources through on-the-job training.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Fukushima University*
JAEA-Review 2023-024, 109 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of methodology combining chemical analysis technology with informatics technology to understand perspectives property of debris and tie-up style human resource development" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to goal of this study is to implement a research plan relate to a development of combinational technology of new chemical analysis with informatics, and the aim is to develop new system for whole image estimation system using small quantities of information.
Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi; Kawata, Manabu; Shiomi, Tadahiko; Li, Y.
JAEA-Research 2024-001, 206 Pages, 2024/03
In the assessment of seismic safety and the design of building structures in nuclear facilities, lumped mass models have been used as standard methods. Recent advances in computer capabilities allow the use of three-dimensional finite element (3D FE) models to account for the 3D behavior of buildings, material nonlinearity, and the nonlinear soil-structure interaction effect. While 3D analysis method has many advantages, it is necessary to ensure its reliability as a new approach. The International Atomic Energy Agency performed an international benchmark study using the 3D FE analysis model for reactor building of Unit 7 at TEPCO's Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Station based on recordings from the Niigataken Chuetsu-oki Earthquake in 2007. Multiple organizations from different countries participated in this study and the variation in their analytical results was significant, indicating an urgent need to improve the reliability of the analytical results by standardization of the analytical methods using 3D FE models. Additionally, it has been pointed out that it is necessary to understand the 3D behavior in the seismic fragility assessment of buildings and equipment, using realistic seismic response analysis method based on 3D FE models. In view of these considerations, a guideline for the seismic response analysis method using a 3D FE model was developed by incorporating the latest knowledge and findings in this area. The purpose of the guideline is to improve the reliability of the seismic response analysis method using 3D FE model of reactor buildings. The guideline consists of a main body, commentaries, and appendixes. The standard procedures, recommendations, key points to note, and technological bases for conducting seismic response analysis on reactor buildings using 3D FE models are provided in the guideline. In addition, the guideline will be revised reflecting the latest knowledge.
Togawa, Orihiko; Hokama, Tomonori; Hiraoka, Hirokazu; Saito, Shota
JAEA-Research 2023-011, 78 Pages, 2024/03
When radionuclides are released into the atmospheric environment at a nuclear emergency, protective measures such as evacuation and temporal relocation are carried out using motor vehicles such as private cars and buses to reduce radiation exposure to residents. To confirm conditions of contamination for the evacuated/relocated residents and the used motor vehicles, contamination inspection is conducted in the middle of the route from border areas of Nuclear Emergency Planning Zone to evacuation shelters. In the present inspection in Japan, a value of OIL4 = 40,000 cpm is used as decontamination criteria. For the details and derivation methods of the value, however, no official documents are found which give systematically detailed descriptions and explanation. It is also recognized that even few experts on nuclear emergencies can explain these subjects in detail as a whole. In order to explain scientifically and technically the OIL4 value of decontamination criteria used in contamination inspection in Japan, this report aims at investigating and estimating the deviation methods of OIL4, and examining and considering these results. To achieve the objectives, we show the bases for decontamination criteria, and investigate and estimate the derivation methods for limits of a surface contamination density corresponding to the generic criteria for each exposure pathway. Moreover, we give the OIL4 value some consideration and suggestions from a viewpoint of positioning and feature of OIL4 in Japan, and cautionary points at revising the value.
Murakami, Kenta*; Arai, Taku*; Yamada, Koji*; Momma, Kensuke*; Tsuji, Takashi*; Nakagawa, Nobuyuki*; Onizawa, Kunio
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2024/03
This paper studied the future vision of codes and standards in Japan by systematically comparing Japanese regulatory rules, standards, and industry guides related to long term operation with international safety standards, and confirmed that the Japanese standard system generally meets their recommendations. The recommendation for the future improvements of Japanese codes and standards were summarized into five items.
Nagata, Hiroshi; Omori, Takazumi; Maeda, Eita; Otsuka, Kaoru; Nakano, Hiroko; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2023-033, 40 Pages, 2024/01
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) was decided as a one of decommission facilities in April 2017. In order to submit the decommissioning plan to the Nuclear Regulation Authority, the type of accident assumed in the first stage of the decommissioning plan was selected, and the public exposure dose was evaluated. A fuel handling accident and a fire accident during storage of waste were selected as assumed accidents in the first stage of the decommissioning plan. An evaluation of the public exposure dose from the radioactive materials released into the atmosphere due to these accidents was estimated to be a maximum of 0.019 mSv (due to a fire accident during storage of waste). This estimated value was found to be sufficiently smaller than the judging criteria (5 mSv), and not to pose a significant risk of radiation exposure to the general public.
Zhang, Y.*; Marusawa, Kenji*; Kudo, Kohei*; Morooka, Satoshi; Harjo, S.; Miyamoto, Goro*; Furuhara, Tadashi*
ISIJ International, 64(2), p.245 - 256, 2024/01
Horii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Furusawa, Naoya*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154799_1 - 154799_20, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The thermal conductivities of near-stoichiometric (U,Pu,Am)O doped with Nd
doped with Nd O
O /Sm
/Sm O
O , which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT)
, which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT) . The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C
. The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C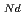 and C
and C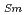 , respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70
, respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70  10
10 + 0.93C
+ 0.93C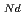 + 1.20C
+ 1.20C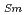 , B(m/W)=2.39
, B(m/W)=2.39  10
10 .
.
Hirota, Noriaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Demura, Masahiko*; Kobayashi, Yoshinao*
The IV International Scientific Forum "Nuclear Science and Technologies"; AIP Conference Proceedings 3020, p.030007_1 - 030007_6, 2024/01
Dynamic strain aging (DSA) and intergranular stress corrosion cracking (intragranular SCC) occur in high temperature pressurized water simulating a boiling water reactor environment due to changes in dissolved oxygen (DO) content, respectively. In order to clearly understand the difference between these phenomena, the mechanism of their occurrence was summarized. As a result, it was found that DSA due to intragranular cracking occurred in SUS304 stainless steel at low DO  1 ppb, while DSA was suppressed at DO 100 to 8500 ppb due to the formation of oxide films on the surface. On the other hand, when DO was increased to 20000 ppb, the film was peeled from the matrix, O element diffused to the grain boundary of the matrix, resulting in intergranular SCC. These results are indicated that the optimum DO concentration must be adjusted to suppress crack initiation due to DSA and intergranular SCC.
1 ppb, while DSA was suppressed at DO 100 to 8500 ppb due to the formation of oxide films on the surface. On the other hand, when DO was increased to 20000 ppb, the film was peeled from the matrix, O element diffused to the grain boundary of the matrix, resulting in intergranular SCC. These results are indicated that the optimum DO concentration must be adjusted to suppress crack initiation due to DSA and intergranular SCC.
Tamura, Koji; Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Oba, Hironori; Karino, Takahiro; Shibata, Takuya; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 8 Pages, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)